As a consumer, you rely on batteries to power a variety of everyday devices, from thermostats to activity trackers, wireless gaming controllers, and so on. Finding the best replacement batteries for these applications can sometimes be a bit confusing, especially when you consider the many different types of batteries available. Today, we will take a close look at two of the most commonly used disposable batteries, alkaline batteries and lithium batteries. We will analyze their differences in terms of performance and cost, and discuss which applications each type of battery is best suited for.
lithium battery vs alkaline battery
lithium battery structure and Working Principle
Lithium battery, officially known as lithium-ion battery (Li-ion battery), is a type of rechargeable battery that primarily rely on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery. During the charging process, lithium ions de-intercalate from the positive electrode and intercalate into the negative electrode through the electrolyte, making the negative electrode lithium-rich; when discharging, lithium ions de-intercalate from the negative electrode and return to the positive electrode through the electrolyte. This back-and-forth movement of lithium ions allows the battery to store and release electrical energy.
advantages and disadvantages of lithium ion battery
Lithium batteries offering the following advantages
- High energy density
- Long cycle life
- Low self-discharge rate
- No memory effect
- Fast charging capability
- Strong environmental adaptability
- Lightweight and miniaturization
- Environmental protection and recyclability
Disadvantages of Lithium-ion Battery
- High cost
- Temperature sensitivity
- Safety risks
- Environmental impact
- Recycling challenges
- Aging issues
- Limited environmental adaptability
Alkaline Battery Structure And Working Principle
Alkaline batteries, also known as zinc-manganese dry cells, are disposable batteries named after their alkaline electrolyte, potassium hydroxide. These batteries consist of three main components: a zinc anode (negative electrode), a manganese dioxide cathode (positive electrode), and potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte. When the battery is discharging, the zinc anode reacts with the electrolyte to produce zincate and hydrogen gas, while the manganese dioxide cathode accepts electrons and reacts with potassium hydroxide to form water and new compounds. This process generates an electric current that powers the external circuit.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alkaline Batteries
Advantages of Alkaline Battery
- Cost-effectiveness
- Stability
- High current output
- Environmental adaptability
- Mercury-free and eco-friendly
- Widely applicable
Disadvantages of Alkaline Battery
- Non-rechargeable
- Lower energy density
- Self-discharge
- Environmental impact
- Performance decline in high temperatures
- Weight and size
Read more: What are Alkaline Batteries
alkaline vs lithium AA batteries
what is Lithium AA batteries
Lithium AA batteries are a type of primary cell battery, which means they are designed for single-use and are not rechargeable. These batteries are known for their remarkable energy density, which is the amount of energy stored in a given system or space. This high energy density is a result of using lithium metal as the anode, which allows these batteries to store more energy compared to traditional alkaline batteries.
Energy Density and Voltage Stability
The energy density of lithium metal batteries is approximately 2-3 times that of alkaline batteries. This means your devices can have a longer lifespan and greater power. Additionally, lithium metal AA batteries maintain a stable voltage of around 1.5 volts throughout their discharge cycle. This stability is crucial for devices that require a consistent power output to function effectively, preventing performance degradation and ensuring smooth operation.
Shelf Life
One of the standout features of Lithium AA batteries is their excellent shelf life. Due to their low self-discharge rate, their charge can be retained for up to 10 years if stored properly. This makes them an ideal choice for emergency equipment and backup power solutions where long-term reliability is essential.
Size and Compatibility
Lithium AA batteries conform to the standard size of AA batteries, making them compatible with a wide range of devices. This universal size ensures that users can easily switch from alkaline to lithium metal batteries without any adjustments or adapters.
Capacity and Performance
The typical capacity of lithium metal AA batteries is around 3000 milliampere-hours (mAh). This capacity allows them to power devices for extended periods, making them particularly suitable for high-drain applications. Increased capacity means fewer battery replacements, reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Environmental Impact
While lithium metal batteries have a higher energy density, their production and disposal can have an environmental impact. Proper recycling of these batteries is crucial to minimize waste and recover valuable materials. Many communities offer specialized recycling programs for batteries to help mitigate environmental impact.

What is an Alkaline Battery
Alkaline batteries, also known as alkaline zinc-manganese batteries, are widely used disposable dry cells. They are favored for their stable voltage output and higher energy density. Alkaline batteries use zinc as the negative electrode, manganese dioxide as the positive electrode, and potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte. This battery design allows them to provide higher voltage and energy output than traditional carbon-zinc batteries during discharge.
Energy Density and Voltage Stability of Alkaline Batteries
While the energy density of alkaline batteries is lower than that of lithium metal batteries, they still offer a relatively high energy output. Their energy density ranges from about 50-100 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), suitable for most household and low-power devices. In terms of voltage stability, alkaline batteries can maintain a voltage of around 1.5 volts throughout their discharge cycle, providing reliable power support for devices that require a stable power supply.
Shelf Life
Alkaline batteries are known for their long shelf life. If stored in a cool, dry place, the charge of alkaline batteries can be retained for several years without significant decline. This makes them an ideal choice for long-term storage or emergency situations.
Size and Compatibility
Alkaline batteries adhere to standard sizes such as AA, AAA, etc., ensuring compatibility with most devices on the market that use these sizes. This standardized size means that users can easily switch between different devices using alkaline batteries without worrying about compatibility issues.
Capacity and Performance
The capacity of alkaline batteries is typically lower than that of lithium metal batteries, but their capacity is still sufficient to meet the needs of most everyday applications. Their typical capacity ranges from a few hundred milliampere-hours to a few thousand milliampere-hours, depending on the size of the battery and the manufacturer. Alkaline batteries perform well in low to moderate discharge rate applications and are suitable for devices such as remote controls, flashlights, and clocks.
Environmental Impact
Although alkaline batteries do not contain harmful substances like mercury, they still have an environmental impact. Other chemical substances in the batteries, such as zinc and manganese, can pollute the environment if not properly managed. Therefore, it is crucial to recycle and dispose of alkaline batteries correctly. Many regions have established battery recycling programs to promote environmentally friendly disposal and recycling of batteries.
Read more:Types of alkaline batteries
Which are better –alkaline battery or lithium?
Most devices are designed to accept one type of battery or the other, not necessarily both. If you’re buying batteries for a specific device, then the best choice will probably be the battery that gets the job done.
That being said, the answer to this question also depends on what your priorities are. If convenience is a priority, then alkaline batteries will probably be your first choice, since they’re more widely available than lithium batteries. They’re also the preferred choice for low-drain devices like smoke alarms, since they have a lower self-discharge rate than the average rechargeable battery.
If you’re looking for great performance or eco-friendliness, then lithium batteries would be the best option. Good-quality li-ion batteries consistently outperform alkalines, and their long lifespans make them much more environmentally friendly than disposable batteries.
Are Regular Batteries Lithium Batteries?
Batteries are an indispensable component of power supply, especially in portable electronic devices. Many people might wonder, “Are regular batteries lithium batteries?” This question involves the basic classification and characteristics of batteries.
Basic Classification of Batteries
Batteries are mainly divided into two major categories: chemical batteries and physical batteries. Chemical batteries generate electricity through chemical reactions, while physical batteries generate electricity through physical changes. In daily life, we most commonly encounter chemical batteries, including alkaline batteries, lithium batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, and so on.
Definition of Regular Batteries
Regular batteries usually refer to the disposable dry cells commonly found in supermarkets and convenience stores, most of which are alkaline batteries. Alkaline batteries are widely used because of their low cost and easy availability. Therefore, when we mention “regular batteries,” we usually mean alkaline batteries, not lithium batteries.
Differences Between Lithium and Alkaline Batteries
Lithium batteries and alkaline batteries have significant differences in chemical composition, voltage, capacity, and application scenarios. Lithium batteries are favored for their high energy density, long life, and low self-discharge rate, while alkaline batteries are widely used because of their low price and easy purchase. The voltage of lithium batteries is typically 3 volts, while that of alkaline batteries is 1.5 volts.
Applications of Lithium Batteries
Due to their high-performance characteristics, lithium batteries are often used in devices that require high energy and long endurance, such as high-end cameras, portable gaming consoles, and some professional equipment. Lithium batteries are also used in devices that have strict size requirements for batteries because of their small volume and weight.
Applications of Alkaline Batteries
In comparison, alkaline batteries are more commonly used for general household and daily purposes, such as remote controls, flashlights, children’s toys, etc. These devices do not have high performance requirements for batteries, and the frequency of battery replacement is relatively fast, making the cost-effectiveness of alkaline batteries higher.
In summary, the answer to the question “Are regular batteries lithium batteries?” is that regular batteries usually refer to alkaline batteries, not lithium batteries. There are clear differences in performance and application between the two. Users should decide which type of battery to use based on the needs of their devices and their budget. With the development of technology, the application of lithium batteries is becoming more and more widespread, but alkaline batteries remain the preferred choice in many scenarios due to their cost-effectiveness.
Do Alkaline Batteries have Lithium?
In today’s rapidly developing battery technology, lithium batteries have become the darling of the market due to their high energy density and long lifespan. However, for traditional alkaline batteries, consumers may wonder: do alkaline batterieshave lithium?
Chemical Composition of Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries, also known as alkaline zinc-manganese batteries, are widely used disposable dry cells. Their name comes from the alkaline electrolyte they use—potassium hydroxide. The three main components of alkaline batteries include:
Anode (negative electrode): Made of zinc, which reacts with the electrolyte during battery discharge, releasing electrons.
Cathode (positive electrode): Made of manganese dioxide, which accepts electrons during battery discharge.
Electrolyte: Potassium hydroxide, which facilitates the chemical reactions inside the battery and acts as a medium for ion transport.
From the above chemical composition, it is clear that alkaline batteries do not contain lithium. Therefore, the answer to the question “Do alkaline batteries have lithium?” is no.
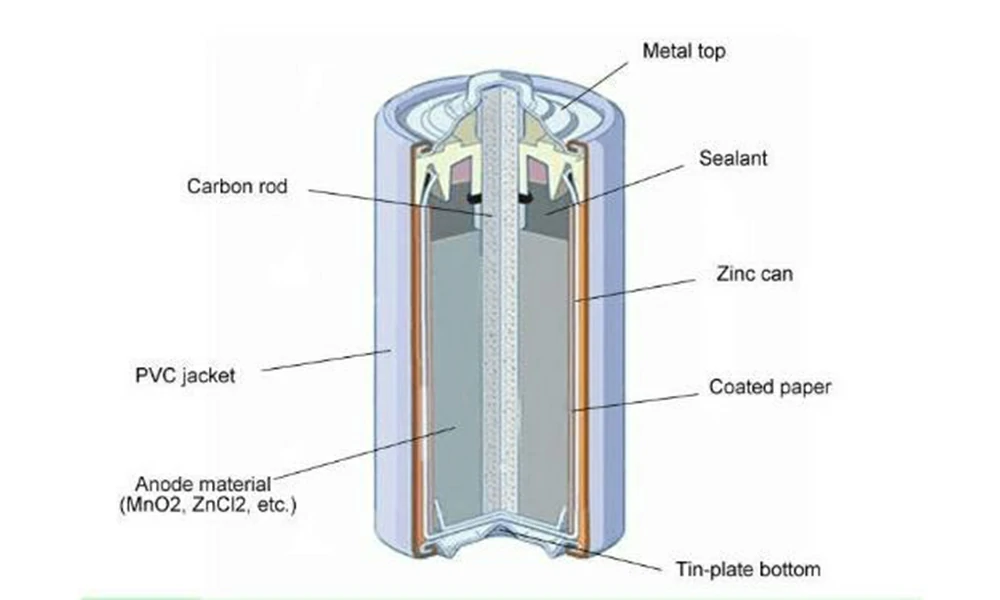
difference between lithium battery and alkaline battery
Although both alkaline and lithium batteries are batteries, they have significant differences in chemical composition and performance:
Chemical composition: As mentioned above, alkaline batteries use zinc and manganese dioxide, while lithium batteries use lithium metal or lithium-containing compounds as their anode materials.
Energy density: The energy density of lithium batteries is about 2-3 times that of alkaline batteries, meaning that lithium batteries can store more energy in the same volume.
Voltage stability: Lithium batteries can maintain a stable voltage of about 3.7 volts throughout their discharge cycle, while alkaline batteries maintain around 1.5 volts.
Environmental impact: Lithium and other metals such as cobalt and nickel in lithium batteries, if not properly managed, may have a greater impact on the environment. In comparison, alkaline batteries do not contain these metals and have a relatively smaller environmental impact.
In summary, alkaline batteries do not contain lithium elements; they are mainly composed of zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide. Although lithium batteries are superior to alkaline batteries in terms of energy density and voltage stability, alkaline batteries remain an economical and practical choice in many application scenarios due to their lower cost and smaller environmental impact. Understanding the chemical composition and performance characteristics of batteries helps us better select the appropriate type of battery to meet different energy needs.
how much longer do lithium batteries last?
Lithium batteries, as the main power source for modern electronic devices and transportation vehicles, have always been a focus for users and manufacturers in terms of their service life. The expected lifespan of lithium batteries is not only related to cost-effectiveness but also to the reliability of the equipment and environmental impact.
Expected Lifespan of Lithium Batteries
The expected lifespan of lithium batteries is typically 2-10 years, a range that depends on various factors, including usage patterns, depth of discharge, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. Compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries can significantly extend their service life with proper care.
Lithium batteries, as the main power source for modern electronic devices and transportation vehicles, have always been a focus for users and manufacturers in terms of their service life. The expected lifespan of lithium batteries is not only related to cost-effectiveness but also to the reliability of the equipment and environmental impact.
Expected Lifespan of Lithium Batteries
The expected lifespan of lithium batteries is typically 2-10 years, a range that depends on various factors, including usage patterns, depth of discharge, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. Compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries can significantly extend their service life with proper care.

Factors Affecting the Lifespan of Lithium Batteries
Battery Chemistry: Different types of lithium batteries have different chemical compositions, and their lifespans vary accordingly.
Usage Patterns: The way a battery is used has a significant impact on its lifespan. Frequent deep discharges and high current consumption can lead to a rapid decline in battery performance.
Environmental Conditions: Temperature is a key factor affecting battery life. Extreme heat can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, leading to faster performance decline.
Charging Habits: Proper charging techniques are crucial for extending battery life. Overcharging or using unsuitable chargers can put stress on the battery and lead to premature failure.
Tips for Extending the Lifespan of Lithium Batteries
- void Deep Discharge: Try to avoid discharging the battery completely, as this can accelerate battery aging.
- Control Charging Temperature: Avoid charging in high-temperature environments to reduce internal pressure and the speed of chemical reactions.
- Use the Right Charger: Use a charger that meets the battery specifications to prevent overcharging.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly check the battery condition and replace damaged or underperforming batteries in a timely manner.
The service life of lithium batteries is influenced by various factors, and their lifespan can be effectively extended through reasonable use and maintenance. Understanding these influencing factors and taking appropriate measures can help users maximize the value of lithium batteries while reducing environmental impact. With technological advancements and the development of battery management technology, the service life of lithium batteries is expected to be further extended.
what is longest lasting battery alkaline or lithium?
In the selection of battery technology, endurance time is a key consideration. Whether it’s remote controls and toys used in daily household life or power demands in professional equipment, the battery’s endurance directly affects the user experience. This article will explore the endurance times of alkaline and lithium batteries to answer the question, “what is longest lasting battery alkaline or lithium?”
Endurance Time of Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries are widely used in daily life for their stable voltage output and higher energy density.In actual tests, some brands of alkaline batteries can have a discharge time exceeding 6 hours, and certain high-performance alkaline batteries can even last 2-3 years in specific appliances. This indicates that alkaline batteries have good endurance in low to medium power consumption devices.
Endurance Time of Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are known for their high energy density and long lifespan. The lifespan of lithium iron phosphate batteries can reach 3000-6000 complete charge and discharge cycles with an annual decay of only 2%. Titanium acid lithium iron batteries can even achieve up to 20,000 charge and discharge cycles. Not only is the endurance time of lithium batteries long, but their low self-discharge rate means that even after long periods of storage, the battery level can remain at a higher level. For example, some thionyl chloride lithium batteries have a shelf life of up to fifteen years, while lithium manganese batteries can last up to ten years. In practical applications, the endurance time of lithium batteries far exceeds that of alkaline batteries, especially in high power consumption devices and scenarios requiring long-term continuous power supply.
The Impact of Environment and Usage Habits on Battery Endurance
The endurance time of batteries is not only affected by the type of battery but also by usage habits and environmental conditions. It is best to keep lithium batteries at 50% charge when not in use for a long time, with a maximum charge of 80% and a minimum discharge of 20% to extend battery life. In addition, lithium batteries are more sensitive to temperature, and a suitable storage and working environment can maximize battery life.
Considering all factors, lithium batteries have a clear advantage over alkaline batteries in terms of endurance time. Whether looking at single-use duration, cycle life, or long-term storage, lithium batteries show longer endurance capabilities. However, when choosing batteries, one must also consider cost, device compatibility, and specific application scenarios. For high power consumption and devices requiring long-term endurance, lithium batteries are a more suitable choice; while for low-cost and low-power daily applications, alkaline batteries remain an economical option. Understanding the endurance characteristics of different batteries can help us better select the appropriate battery type based on actual needs.

